AMD EPYC “9006” Embedded Venice CPUs Boast 96 “Zen 6” Cores & PCIe Gen6, EPYC Embedded 2005 “Fire Range” & Annapurna Families Unveiled
AMD is gearing up to expand its EPYC Embedded family with new offerings such as the Venice “Zen 6” series, the Fire Range “Zen 5” series, and the Annapurna lineups. These developments come as the company continues to innovate in the processor market, promising enhancements in performance and efficiency.
Unveiling the Next-Gen AMD EPYC Embedded CPUs
Recent reports reveal that AMD’s EPYC Embedded family, including the 4005 lineup, is based on the Granite Ridge “Zen 5” architecture, featuring up to 16 cores and PCIe Gen5 support. Meanwhile, the high-end “Genoa” lineup boasts up to 192 “Zen 5” cores, offering 512 MB of L3 cache and 128 PCIe Gen5 lanes. These have been available for some time, but AMD is gearing up to introduce new families including EPYC Embedded Venice, 4005 Series, and Annapurna, each targeting different market segments.

The EPYC Embedded Venice family stands out with up to 96 “Zen 6” cores, PCIe Gen6, and DDR5/MRDIMM support, making it a part of the EPYC Embedded “9006” series. The Fire Range series, aimed at mid-range platforms, offers up to 16 “Zen 5” cores, leveraging PCIe Gen5 and DDR5-5600. These chips are adapted from desktop dies used in the Ryzen 9000HX mobile family, targeting sectors like Networking, Storage, and Industrial use.
Insights into AMD’s Annapurna and Future Prospects
The EPYC Embedded Annapurna series is designed for optimal performance in Network Control planes, providing exceptional performance per watt and cost efficiency, suitable for entry-level switches, routers, and security applications. While details on the core architecture are still forthcoming, these developments highlight AMD’s commitment to the Embedded market.
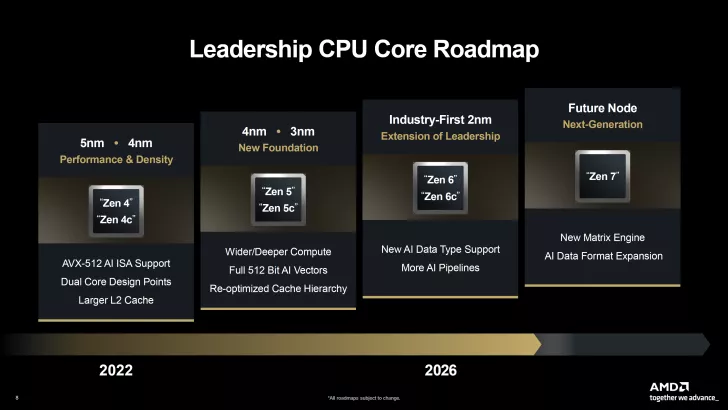
Anticipation is building as AMD plans to launch these cutting-edge EPYC Embedded platforms in 2026-2027, aiming to solidify its presence in the ever-evolving Embedded market landscape.