Intel Diamond Rapids “Xeon” CPUs Boast Unique CBB and IMH Tile Design
Intel’s upcoming Diamond Rapids “Xeon” CPUs are generating buzz with the introduction of two new and distinct tiles named CBB and IMH. These innovations signal a significant shift in the architecture design of Intel’s next-gen processors, aiming to enhance performance and efficiency for data centers.
Revolutionary Tile Design in Diamond Rapids
Reports suggest that Intel’s Diamond Rapids will feature a groundbreaking architecture with two new tiles. The CBB, or “Core Building Block,” will serve as the primary compute tile. Unlike its predecessor Granite Rapids, Diamond Rapids will separate the integrated memory controller (IMC) onto a different tile. This new tile, known as the IMH or “Integrated I/O & Memory Hub,” will host the IMC, and it’s anticipated that up to two of these IMH dies could be featured in the new CPUs. Sources have stated the IMH die will be positioned on the base tile, adopting a design approach similar to the Clearwater Forest.
Technical Enhancements and PCIe Gen6 Support
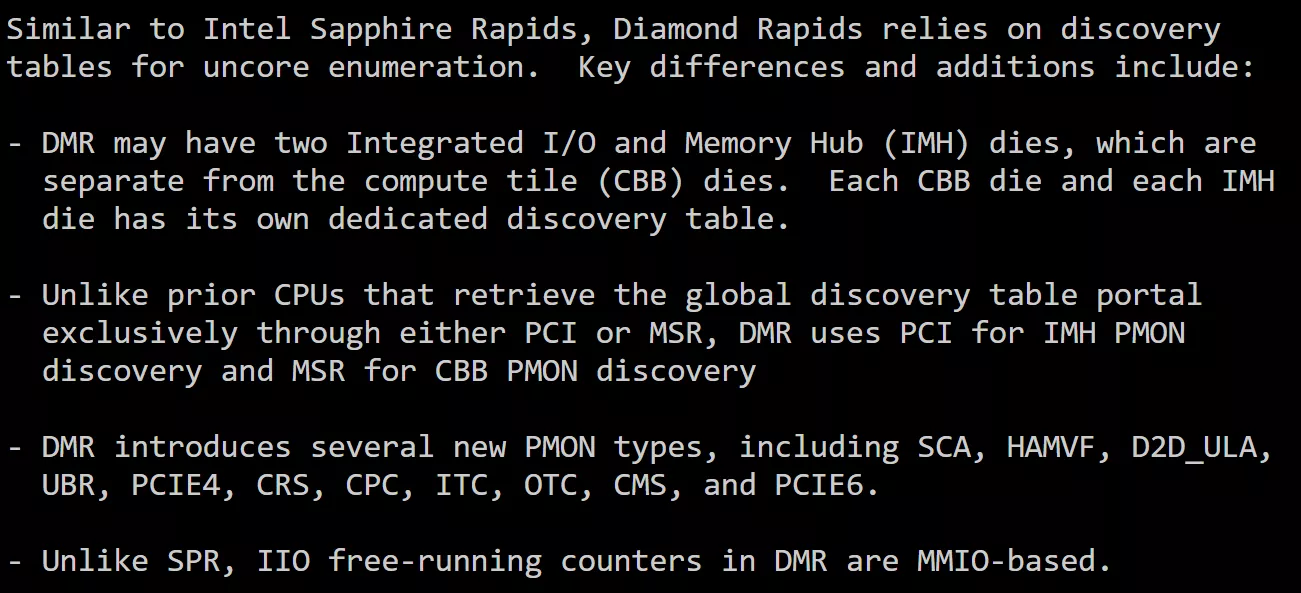
Similar to Intel Sapphire Rapids, Diamond Rapids relies on discovery tables for uncore enumeration. Key differences and additions include:
- DMR may have two Integrated I/O and Memory Hub (IMH) dies, which are separate from the compute tile (CBB) dies. Each CBB die and each IMH die has its own dedicated discovery table.
- Unlike prior CPUs that retrieve the global discovery table portal exclusively through either PCI or MSR, DMR uses PCI for IMH PMON discovery and MSR for CBB PMON discovery
- DMR introduces several new PMON types, including SCA, HAMVF, D2D_ULA, UBR, PCIE4, CRS, CPC, ITC, OTC, CMS, and PCIE6.
- Unlike SPR, IIO free-running counters in DMR are MMIO-based.
With the inclusion of PCIe Gen6 support, the Diamond Rapids series is set to align with other next-gen data center CPU platforms launching this year, such as Venice. These enhancements are poised to provide significant performance improvements, making them highly anticipated in the tech community.
Expectations and Future Release
Intel’s Diamond Rapids “Xeon” CPUs are expected to boast impressive specifications, with potential configurations reaching up to 192 cores or even 256 cores, though official confirmation is still pending. These CPUs are expected to operate on the advanced 18A process node and incorporate Panther Cove P-Cores. Early insights into platform details suggest TDPs of up to 650W on the LGA 9324 platform, which will support multi-socket capabilities. Intel plans to unveil its Diamond Rapids CPUs by mid to late 2026, marking a significant leap in processor technology for data centers.