In a significant shift in its server processor strategy, Intel has decided to streamline its focus towards higher memory bandwidth solutions. The tech giant has made an unexpected move by canceling its 8-channel Diamond Rapids server processors. This decision aims at enhancing performance to cater to the demanding needs of modern data centers.
Intel’s Shift to 16-Channel Focus
According to reports, Intel’s strategic overhaul is influenced by changes in its Data Center Group leadership, impacting the next-generation Xeon 7, or Diamond Rapids. Intel has announced the discontinuation of its 8-channel Diamond Rapids series, originally expected to follow the Xeon 6 or Granite Rapids-SP processors. The decision is based on the growing memory demands in server markets, where the 8-channel version no longer meets industry needs.
Intel stated, “We have removed Diamond Rapids 8CH from our roadmap. We’re simplifying the Diamond Rapids platform with a focus on 16 Channel processors and extending its benefits down the stack to support a range of unique customers and their use cases.”
The Benefits of 16-Channel Architecture
Focusing on the 16-channel Diamond Rapids, Intel aims to leverage increased memory capacity and bandwidth to support next-generation workloads. The 16-channel design is expected to overcome the limitations of the 12-channel variant, offering superior bandwidth, density, and I/O capabilities to support scalable data-center operations.
Modern workloads like AI training and large-scale virtualization demand significant memory bandwidth, making the 16-channel setup an ideal choice. Reports suggest that the 16-channel Diamond Rapids may support memory frequencies up to 12,800 MT/s, delivering an impressive 1.6 TB/s of memory bandwidth.
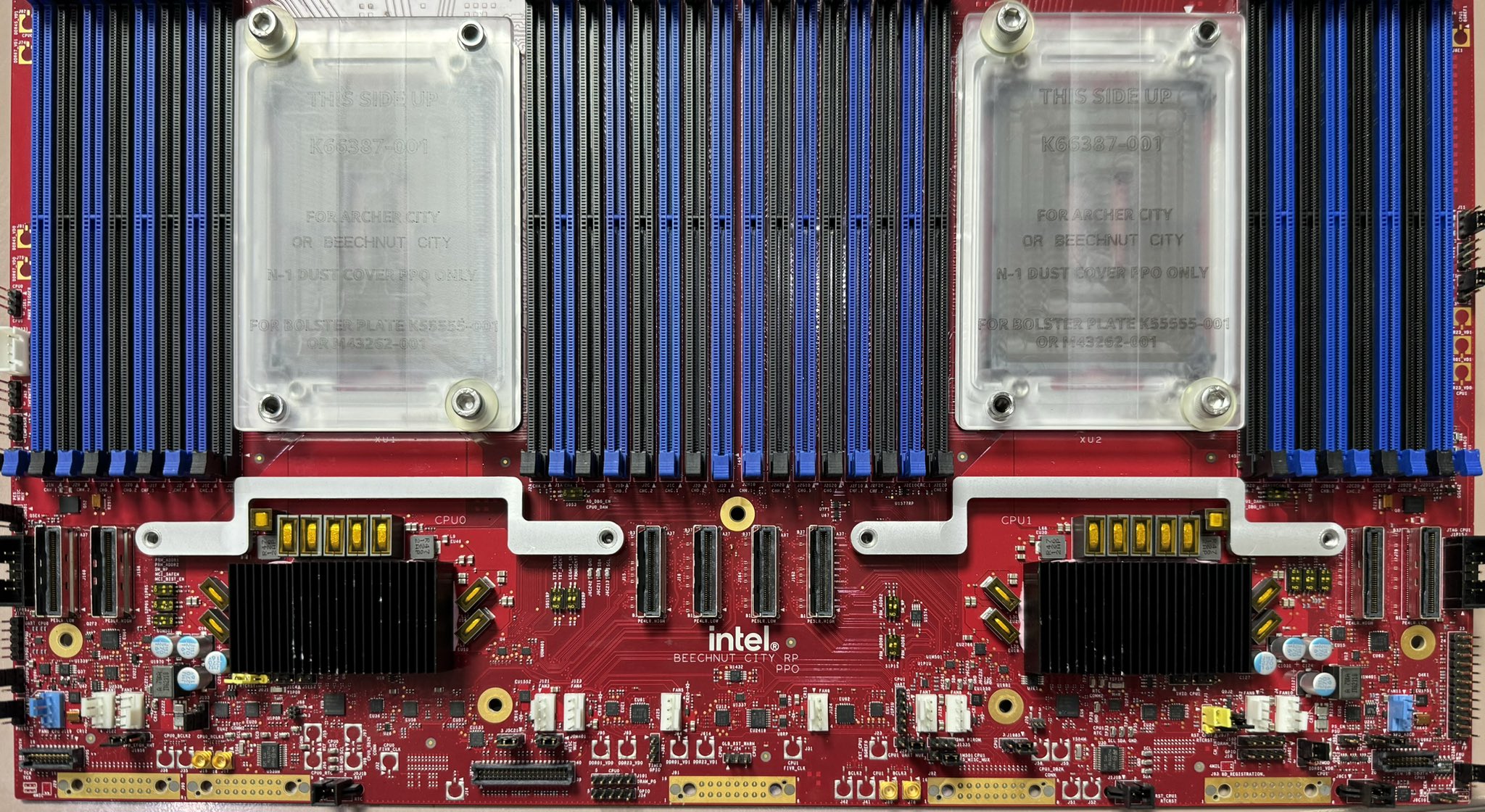
Positioning Against Competition
Intel’s move is also a strategic response to AMD’s EPYC series, which is advancing towards high memory-channel counts as well. To maintain and potentially grow its market share in server CPUs, Intel’s adoption of the 16-channel configuration is seen as a critical step. While the 8-channel design was more cost-effective, its relevance diminishes with increasingly demanding workloads. Intel’s decision to prioritize a balance between performance and cost with the 16-channel approach is expected to position it competitively against AMD in the server market.
