Intel Xeon 696X 64-Core Granite Rapids-WS CPU Benchmark Revealed: Falls 27% Behind 64-Core Ryzen Threadripper PRO 9985WX
In the competitive realm of high-performance CPUs, Intel’s Xeon 696X has made a splash by emerging in leaked benchmarks. Despite boasting an impressive array of features, it appears to fall short when compared to AMD’s Threadripper alternatives. As Intel continues to refine its offerings, the tech community eagerly anticipates what the Granite Rapids-WS lineup might bring to the table.
Intel Xeon 696X: A Powerhouse with 64 Cores
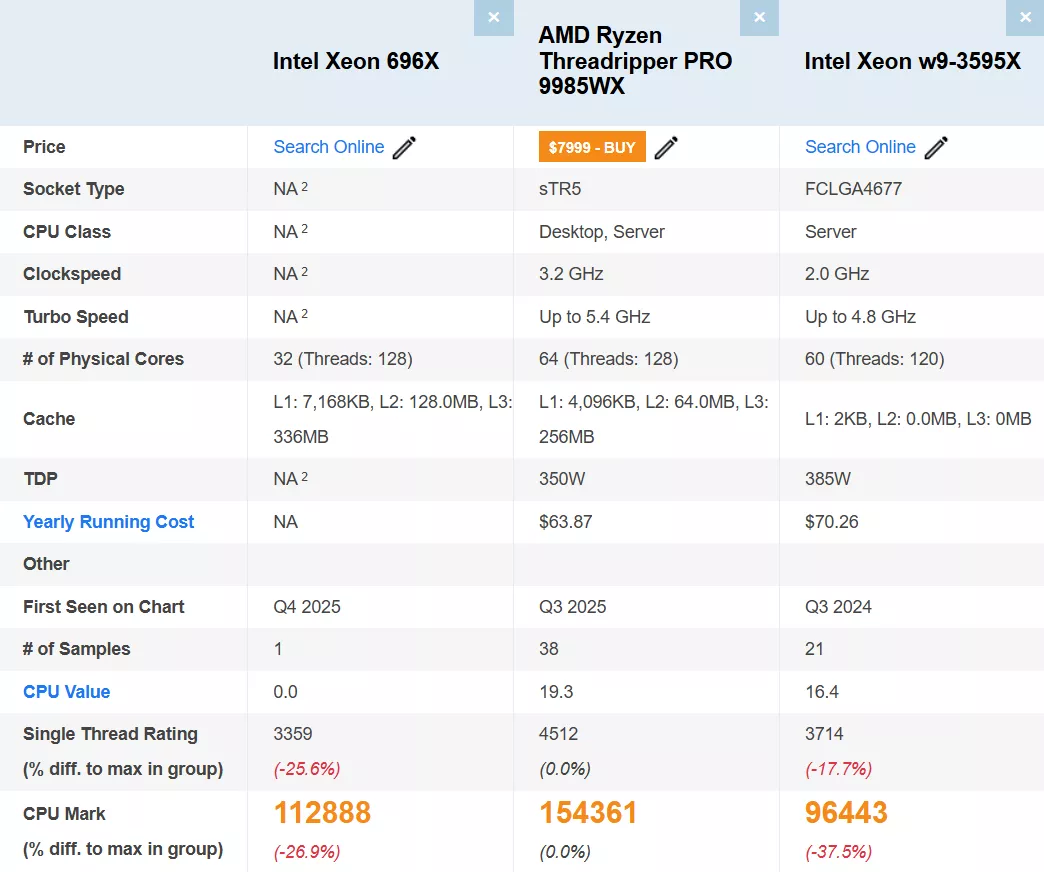
The Intel Xeon 696X CPU, a high-end model from the Granite Rapids-WS series, recently surfaced in leaked benchmarks, offering insights into its specifications and preliminary performance. Initially revealing itself a few weeks ago, this chip reappeared in the PassMark Software database. Although initially misreported as a 32-core model, it’s clear that the Xeon 696X is equipped with 64 cores and 128 threads, built on the Redwood Cove P-Core architecture. It features an impressive 336 MB of L3 cache and operates at a base clock speed of 2.4 GHz, boosting up to 4.6 GHz.
Performance Insights and Comparisons
The specifications of the Xeon 696X already surpass the earlier “Sapphire Rapids-WS” flagship, the Xeon W9-3595X, which offers 60 cores and 120 threads. With TDPs of 350W at base, the Granite Rapids-WS series is expected to reach 450-500W at its maximum turbo power, an increase from the previous generation’s 462W.
In benchmark tests, the Xeon 696X scored 3359 in single-core and 112,888 in multi-core tests, trailing 27% behind the AMD Ryzen Threadripper PRO 9985WX, which also sports 64 cores powered by Zen 5 architecture. This CPU, however, shows a 17% improvement over the Xeon W9-3595X, although the single-threaded performance lags behind, suggesting these might be early engineering samples. As the final retail versions become available, better performance is anticipated.
0
25727
51454
77181
102908
128635
154362
Looking Ahead: Intel’s Future Plans
Intel is anticipated to reveal its next-generation workstation lineup in the coming year, potentially at CES 2026. This forthcoming unveiling could offer deeper insights into the capabilities of the Granite Rapids family and how it intends to challenge AMD’s offerings in the high-performance CPU market.
| CPU Name | Cores / Threads | Clock (Base / Boost) | L3 Cache | TDP |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Xeon 698X | 86 / 172 | 2.0 / TBD | 336 MB | 350W |
| Xeon 696X | 64 / 128 | 2.4 / 4.6 | 336 MB | 350W |
| Xeon 678X | TBD | 2.4 / TBD | 192 MB | 350W |
| Xeon 676X | TBD | 2.8 / TBD | 144 MB | 350W |
| Xeon 674X | TBD | 3.0 / TBD | 144 MB | 350W |
| Xeon 658X | TBD | 3.0 / TBD | 144 MB | 350W |
| Xeon 656 | TBD | 2.9 / TBD | 72 MB | TBD |
| Xeon 654 | 18 / 36 | 3.1 / 4.6 | 72 MB | TBD |
| Xeon 638 | TBD | 3.2 / TBD | 72 MB | TBD |
| Xeon 636 | TBD | 3.5 / TBD | 48 MB | TBD |
| Xeon 634 | TBD | 2.7 / TBD | 48 MB | TBD |